Lymphome de Hodgkin – TEP en position de traitement de radiothérapie
Pour les patients atteints de lymphome de Hodgkin localisé sus-diaphragmatique la TEP est réalisée avant traitement en position de radiothérapie. La concertation avec l’équipe spécialisée est nécessaire pour solliciter le binôme médecin nucléaire – radiothérapeute.
Lymphome de Hodgkin, mise en place de la radiothérapie nodale par le radiothérapeute et le médecin nucléaire
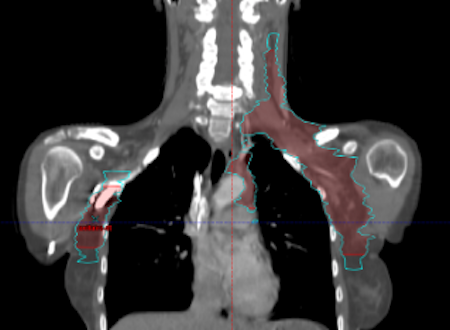
Dans le cadre du bilan initial du lymphome de Hodgkin classique doit être réalisé un scanner diagnostic injecté ainsi qu’une TEP. En cas de stades I et II sus-diaphragmatiques, le traitement standard repose sur la chimiothérapie suivie d’une radiothérapie de clôture. Afin de limiter les possibles conséquences de la radiothérapie, les volumes ont été réduits et les techniques modernes d’irradiation intégrées dans les soins courants. L’essai H10 EORTC/LYSA/FIL a introduit un nouveau concept de radiothérapie : l’irradiation nodale ou radiothérapie « involved node » qui permet une limitation des champs de traitements aux adénopathies présentes avant la chimiothérapie. Afin de mettre en place cette technique d’irradiation, il est impératif que la TEP soit effectuée non pas les bras levés au-dessus de la tête (position habituelle de la TEP), mais en position de traitement de radiothérapie, les bras le long du corps légèrement écartés, avec un masque de contention de la tête, du cou et des épaules, adapté à la morphologie du patient. Au moment du scanner dosimétrique de radiothérapie réalisé avec le masque de contention, une fusion minutieuse sera effectuée avec la TEP initiale. Les volumes d’irradiation correspondent aux adénopathies avant chimiothérapie dans le sens cranio caudal et sont adaptés en latéral et en antéro-postérieur aux déplacements tissulaires (excluant les structures adjacentes normales : musculaires, parenchymateuses, osseuses ou vasculaires) induits par la réduction souvent importante de taille des ganglions après chimiothérapie.
En l’absence de TEP initiale en position de traitement sera réalisée une radiothérapie de type « involved-site » qui comprend une extension de volume de radiothérapie de 1,5 cm en cranio-caudal. (figure 2)
Rédaction avec la participation de :
Dr Karine Peignaux-Casasnovas, Département d’oncologie radiothérapie, Centre Georges-François Leclerc, Dijon.
Dr Alina Berriolo-Riedinger, Service de Médecine Nucléaire, Centre Georges-François Leclerc, Dijon.
TEP en position de traitement de radiothérapie

Radiothérapie “involved-node” (rouge) et “involved-site” (bleu)
Références
André MP, Girinsky T, Federico M, et al. Early Positron Emission Tomography Response-Adapted Treatment in Stage I and II Hodgkin Lymphoma: Final Results of the Randomized EORTC/LYSA/FIL H10 Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jun 1; 35(16):1786-1794.
Barillot I, Mahé MA, Antoni D, Hennequin C. Radiotherapy of lymphomas. Cancer Radiother. 2016 Sep; 20 Suppl: S244-8.
Édeline V, Remouchamps V, Isnardi V, Vander Borght T. Multimodality imaging using PET/CT (18F)-fluorodeoxyglucose for radiotherapy field delineation of localized Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Radiother. 2018 Sep;22(5):384-392.
Girinsky T, Specht L, Ghalibafian M, Edeline V, Bonniaud G, Van Der Maazen R, Aleman B, Paumier A, Meijnders P, Lievens Y, Noordijk E, Poortmans P; EORTC-GELA Lymphoma Group. The conundrum of Hodgkin lymphoma nodes : to be or not to be included in the involved-node radiation fields. The EORTC-GELA lymphoma group guidelines. Radiother Oncol. 2008 Aug; 88(2):202-10.
Girinsky T, Aupérin A, Ribrag V, Elleuch M, Fermé C, Bonniaud G, Ruelle C, Alberini JL, Celebic A, Edeline V. Role of FDG-PET in the implementation of involved-node radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 Aug 1;89 (5):1047-52.
Hoskin P.J., Diez P., Williams M., Lucraft H., Bayne M. Recommandations for the use of radiotherapy in nodal lymphoma. Clin Oncol 25 (2013): 49-58.Specht L, Yahalom J, Illidge T,et al. Modern radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma: field and dose guidelines from the international lymphoma radiation oncology group (ILROG). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 Jul 15; 89(4):854-62n.
Specht L, Yahalom J. The concept and evolution of involved site radiation therapy for lymphoma. Int. J. Clin Oncol 2015; 20:849-854.
Swerdlow AJ, Cooke R, Bates A, et al. Breast cancer risk after supradiaphragmatic radiotherapy for Hodgkin’s lymphoma in England and Wales: a National Cohort Study. J Clin Oncol. 2012 Aug 1; 30 (22):2745-52.
Van Nimwegen FA, Schaapveld M, Cutter DJ, et al. Radiation Dose-Response Relationship for Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Survivors of Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016 Jan 20; 34 (3):235-43.
